What is RPA
RPA is a software program that can automate manual processes. Most of the implementation of RPA solutions are non-invasive type, which means it allows other systems to operate without constraining their capabilities. Automation software functions as a robot that executes jobs in the system by impersonating humans’ work automation. It is famous for its front-end to support business processes since non-IT people are able to design, deploy, and use the solution without sufficient technical and coding skills and focus on the process solution rather than technical infrastructure. RPA supports as a component between human workers and business process automation where it is implemented in the case where human and integration of business process management systems (BPMS) need a huge amount of effort and expense and that is not acceptable to business needs. RPA software market continues to increase, from 1.26 billion USD in 2020 to 1.61 billion USD in 2021, and is projected to have a rise in end-user spending worldwide by 17.5% in 2023.
RPA has three types of automation, namely; Attended Automation, Unattended Automation, and Hybrid Automation. The difference between the three lies in user intervention in executing the automation process. Attended Automation works directly on the user’s computer and requires user intervention to manually trigger the start of the automation process. Attended Automation can respond directly to user requests so it is often used as a personal assistant for users in carrying out daily repetitive work without being controlled by a specific schedule. Meanwhile, Unattended Automation usually works on a server that has been designed to run the automation process automatically, so it does not require user intervention to start the automation process. The last type, namely Hybrid Automation, is a combination of Attended Automation and Unattended Automation. This type of automation is suitable for business processes that require final confirmation regarding the results of the RPA robot’s work.
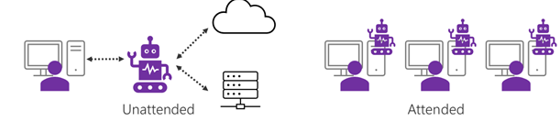
Figure 2. Unattended Automation and Attended Automation Visualization
Each type of automation has its advantages. In general, the advantage of implementing Attended Automation lies in its fast implementation time, so that it can coordinate simple repetitive jobs quickly. Apart from that, implementing Attended Automation also does not disrupt existing workflows. However, Attended Automation still requires user intervention in its implementation so it is not suitable for jobs that require availability 24 hours a day and 7 days a week. Unattended Automation usually runs on an organization’s server by ignoring user intervention or intervention in the process, so this type of automation can operate without stopping. Unattended Automation can also be controlled and monitored remotely so it is superior to Attended Automation which can only work on the user’s computer. Implementing Unattended Automation in an organization can increase the optimality of business processes and has the opportunity to produce a higher Return on Investment (ROI). Besides categorizing RPA based on the need for human intervention, currently, RPA is also able to work on task that requires intelligence, which commonly refers as intelligent RPA (IRPA) or cognitive RPA. Cognitive automation is the type of automation that utilizes machine learning to automate task that requires knowledge which is based on applying artificial intelligence that mimics human intellect.
In general, RPA technology can reduce manual tasks, decrease human resource-related expenses by up to 50%, and decrease transaction processing expenses by up to 60%. This is possible because the ‘bot’ can work 24/7 and can execute jobs quicker than humans. However, of course, the implementation will be more complex and require a structured business flow. RPA implementation tends to have lower cost and effort compared to whole enterprise system implementation. It usually takes time below a month. However, RPA has a number of limitations, such as; it is usually only suitable for rule-based tasks processes; may be a temporary answer that only automates manual processes based on the old IT systems; increasing the complexity of the process since some processes are still executed by a human, and require new task to be performed by the employees to review and supervised robot’s job.
Sumber:
Wijaya, Mahaning. I., and Gunawan, Ali, 2024.


