Using database for business intelligence and analytics
1.1 INTRODUCTION
What is a database? Database is an electronic collection of structured data, usually kept in an ordered manner within a computer system. The database has been around for more than 50 years and has been used by many companies to store important information such as transactions, employee’s data, other company activities but also to reduce data redundancy.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of business, the role of data has become central to driving decisions, strategies, and long-term planning. Databases, particularly those like MySQL and SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), have played a pivotal role in business intelligence (BI) and analytics, transforming raw data into valuable insights.
With the excessive amount of data in the digital age, businesses are increasingly turning towards data-driven strategies. Database is the heart of this transformation. It provides a structured way to store, retrieve, and manage data. MySQL, an open-source relational database, and SSMS, a component of Microsoft SQL Server for managing databases, are widely used tools in businesses. (The picture below is based on 6sense.com, link can be obtained from below)
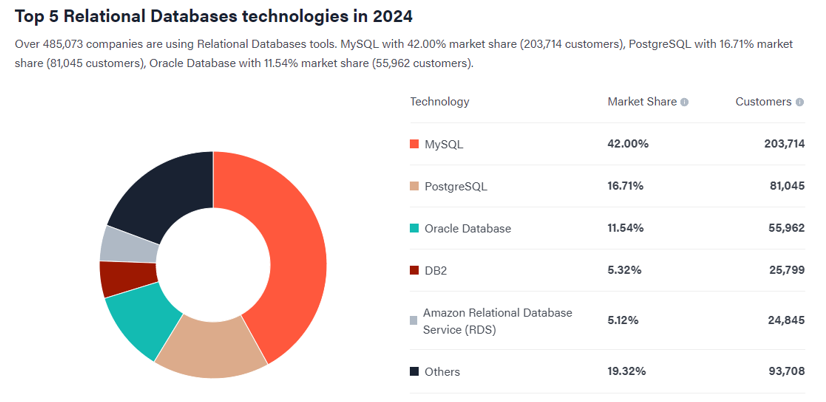
BODY
2.1 MySQL and SSMS Abilities:
MySQL is known for its speed and reliability. It has been the popular choice for businesses needing a robust database solution. Its ability to handle large volumes of data efficiently makes it ideal for BI purposes. This is because MySQL facilitates the storage and retrieval of large datasets that businesses use to track various metrics and trends.
For instance, big companies like Amazon use MySQL to store customer data, purchase histories, and product information. By analyzing these data, businesses can uncover patterns in customer behavior, identify popular products, and optimize their marketing strategies.
On the other platform like SQL Server Management Studio, it can provide a more comprehensive environment for managing SQL Server infrastructure. It is capable to maintain databases that hold critical business data because SSMS allows for easy querying, analysis, and visualization of data, which is crucial for BI (Business Intelligence) tasks.
2.2 Integrating both MySQL and SSMS for business intelligence.
What makes MySQL and SSMS even more powerful in the context of Business Intelligence and analytics is their ability to integrate with various Business Intelligence tools. Tools like Tableau or Qlik can connect to these databases to extract data, which can then be transformed into interactive dashboards and reports. A good example of this is combining Tableau with data from MySQL to make a dashboard like the image below:
(Covid Case)
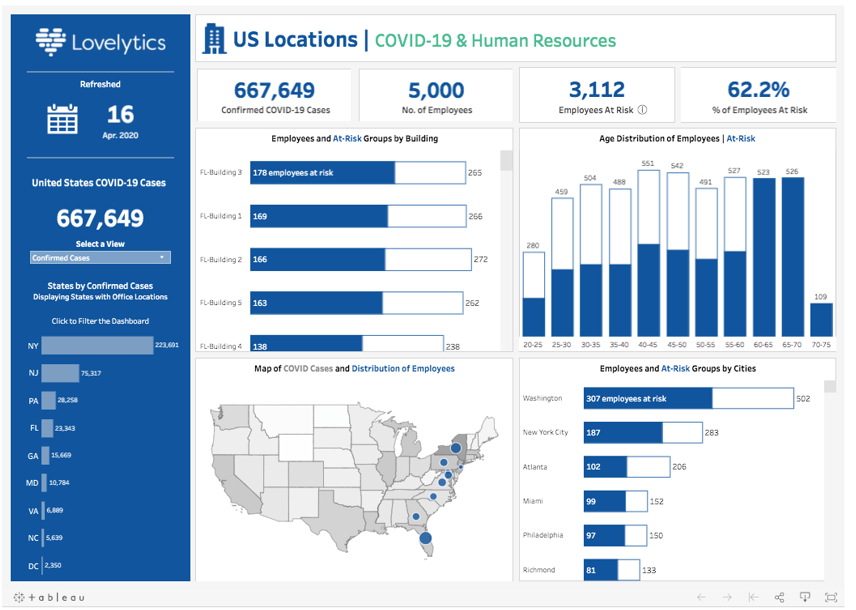
This integration allows businesses to visualize their data in a more meaningful way, making it easier to identify upcoming trends, forecast future outcomes, and make informed decisions for the company. For instance, a business could use these tools to visualize sales data from MySQL in real-time, enabling quick responses to market changes.
2.3 Database Challenges and Considerations
The use of databases for Business Intelligence and analytics must consider challenges. Database must ensure data quality, manage large volumes of data, and maintain data security to avoid data redundancy and duplication. Therefore, companies must implement robust data governance and security protocols to protect sensitive information.
Moreover, the choice between MySQL and SSMS, or any other database, often depends on specific business needs, such as existing infrastructure, and budget constraints. Businesses must evaluate their requirements carefully to choose the most suitable database solution.
3.3 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, databases like MySQL and SSMS are invaluable for businesses looking to leverage BI and analytics. They provide the necessary infrastructure to store, manage, and analyze data, turning it into actionable insights. As businesses continue to navigate a data-centric world, the strategic use of these databases will be a key determinant of their success.
References:
- Alfian Dharma Kusuma (2020). Apa itu Database? Contoh Produk dan Fungsinya. DicodingIntern. Accessed from: https://www.dicoding.com/blog/apa-itu-database/
- https://6sense.com/tech/relational-databases
- NetSquare Technologies (2022). Mysql: The Most Popular Database Management System. Accessed from: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/mysql-most-popular-database-management-system-netsqure#:~:text=variety%20of%20formats.-,Mysql%20is%20the%20most%20popular%20database%20management%20system.,used%20by%20millions%20of%20websites.
- Stan de Boisset (2020). 6 dashboards from Tableau partners to help you mitigate COVID-19 impact. Tableau. https://www.tableau.com/blog/6-dashboards-tableau-partners-help-you-mitigate-covid-19-impacts


