The Role of Data Warehouses in Business Intelligence
Keywords: datawarehouse, Business Intelligence, database, ETL
As the technological era develops, the economic ecosystem requires exploration and learning using raw data for core competencies. To focus on organizational learning and competitive advantage, many organizations will achieve successful outcomes because they can quickly respond to customer demands and become more adaptable to the current business market as a result of their ability to adapt to the changing conditions of the business environment (Martins et al., 2020). In addition, business or organizations must determine what has to be done, how to accomplish it, and how to carry out the essential tasks (Martins et al., 2020). Thus, combining techniques, including Business Intelligence and Data Warehousing, is required to handle and retain information and make the best possible decisions.
Business Intelligence is an architecture created to function as an application that offers databases and decision-making rather than a product (Ramadhan et al., 2022). Business Intelligence is widely recognized for its application in business and organizations due to its capacity to leverage stored data from various sources through mathematical and analytical models (Ramadhan et al., 2022). This data is then managed into a series of reference business information for analysis, supporting intricate decision-making processes and actions to attain firm performance that can adjust to company goals (Ramadhan et al., 2022). Naturally, businesses or organizations that need to make decisions at a higher level will find this to be quite helpful (Ramadhan et al., 2022). However, using a system known as a Data Warehouse, whose job is to gather and analyze data stored into quality decisions, can make processing different data a lot more efficient (Ramadhan et al., 2022).
A Data Warehouse is a system designed to hold and manage a collection of firm data by adding new records instead of updating old ones with new information (Iraza & Nasution, 2023). It can be defined as a large-capacity data storage system that supports management decision-making by generating new records. As such, a Warehouse is subject-oriented and time-variant (Wahono & Ali, 2021).
Data Warehouse and Business Intelligence might have similar uses, but the two tools differ (Ramadhan et al., 2022). Still, there is a relationship between these two tools, such as interrelated process (Ramadhan et al., 2022). The accompanying picture below might explain the process of managing Business Intelligence with Data Warehousing in it to help better understand the context:
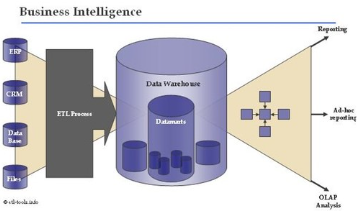
Figure 1 Business Intelligence Process (Source: https://fluxicon.com/blog/assets/2011/01/business_intelligence.jpeg)
The Business Intelligence management process is generally broken down into three parts, further explained by Martins et al. (2020). Namely, the first part, which is referred to as Data Collection, is divided into ETL (Extraction, Transforming, and Loading) stages with explanations as follows:
- Extraction gathers relevant data from various internal and external sources of organizations’ businesses.
- Transforming is converting and adjusting data to the Data Warehouse target format.
- Loading, which is the loading phase that involves recording or updating data that has been collected and converting it into a Data Warehouse.
The processes that have reached the Data Warehouse’s storage stage are included in the second part, which is referred to as the Consolidation/Storage Processes (Martins et al., 2020). After collecting information through ETL techniques, the data will be allocated to the Data Warehouse and Data Marts (Martins et al., 2020). The Data Warehouse enables analysis to occur, as it transforms unusable or underaccessible data into useful information that is helpful for business strategy (Martins et al., 2020).
The third part, or Data Analysis and Distribution, is the stage of data mining, OLAP, reporting, and making decisions to support the provision of high-quality data representation and visualization (Martins et al., 2020).
The explanation above makes it clear that the Data Warehouse is subject-oriented in addition to storing information since it may address the needs of high-quality decision-making by storing relevant information about the core of the business (Martins et al., 2020). Apart from that, research by Martins et al. (2020) has demonstrated that Data Warehouses have several other advantageous features, such as:
- Uniquely representing data by converting data from multiple company systems to make it more integrated.
- The value of the stored data will remain the same over time.
- Granularity by what is contained in the Data Warehouse.
In this sense, discussions related to Business Intelligence, a tool used to help an organization or corporation make the best decisions, and Data Warehouses are tightly tied to each other.
References
Garani, G., Chernov, A. V., Savvas, I. K., & Butakova, M. A. (2019). A Data Warehouse Approach for Business Intelligence. 2019 IEEE 28th International Conference on Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises (WETICE), 70–75. https://doi.org/https:doi.org//10.1109/WETICE.2019.00022
Iraza, K., & Nasution, M. I. P. (2023). MENINGKATKAN DAYA SAING BISNIS : PERAN DATA DALAM PENGAMBILAN KEPUTUSAN. Jurnal Sains Student Research, 1(2), 888–894. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.61722/jssr.v1i2.329
Martins, A., Martins, P., Caldeira, F., & Sá, F. (2020). An Evaluation of How Big-Data and Data Warehouses Improve Business Intelligence Decision Making. In J. Kacprzyk, Á. Rocha, L. P. Reis, I. Orovic, H. Adeli, S. Costanzo, & F. Moreira (Eds.), Trends and Innovations in Information Systems and Technologies (Vol. 1, pp. 609–619). Springer. https://doi.org/https:doi.org//10.1007/978-3-030-45691-7
Ramadhan, H. F., Fauzi, A., Rupelu, C. N., Aprillia, D. P., Anjani, N. D., & Halimatusadiah. (2022). PENGARUH BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE TERHADAP PERUSAHAAN DALAM PENGAMBILAN KEPUTUSAN: BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE, ARSITEKTUR BI DAN DATA WAREHOUSE (KAJIAN STUDI BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE). Jurnal Ekonomi Manajemen Sistem Informasi, 3(6), 639–644. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.31933/jemsi.v3i6
Wahono, S., & Ali, H. (2021). PERANAN DATA WAREHOUSE, SOFTWAREDAN BRAINWARETERHADAP PENGAMBILAN KEPUTUSAN (LITERATURE REVIEW EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SISTEM FOR BUSINESS). Jurnal Ekonomi Manajemen Sistem Informasi, 3(2), 225–239. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.31933/jemsi.v3i2


