Backup and Recovery Strategies For Databases
Backup and recovery are creating duplicate and updating multiple copies of data regularly and keeping them in another one or more remote locations beside the location of the main database for safety measures. Then recovery is recovering the data loss caused by disasters, such as a damaged file, data corruption, cyberattacks, or natural disasters. We refer to the process of creating copies of data as a backup. At the same time, disaster recovery is the strategy and procedures used to immediately restore access to the company’s data following a data loss caused by a system disruption. This strategy may include transferring to other alternative servers and storage devices until the primary data center can be restored. More than simply having data backups is required to fix the business operation. That is why having a backup and disaster recovery plan is extremely important to keep the company running.
Type of Backup

Full backups—Full backups create and update duplicate data in another place beside the main server or system. For a simple analogy, think of saving all your work folders in another drive. Full backups protect every bit of data from a single server, database, virtual machine (VM), or data source connected to the network.
Incremental backups—Think of incremental backups as adding or updating more data since your last backup. An incremental backup captures only new data since the previous full backup was performed.
Differential backups—Like incremental backups, Differential backups are a backup method that only backs up the data that has changed since the last full backup. Think of this backup as what’s different from the last time you did a full backup of the work folder.
Granular recovery of files, folders, and objects—Also known as file-level or object-level recovery, this is the process of quickly recovering one or just a few specific data sets from among many volumes.
Instant mass restore–This process allows IT staff to recover not just files but hundreds of virtual machines (VMs) instantly, at scale, to any point in time, saving time and resources.
Volume recovery—Process teams that need to recover an unlimited number of VMs at the same time use volume recovery for faster recovery, for example, all VMs belonging to an application group.
Virtual Machine Disk (VMDK) recovery – This recovery process ensures all data and apps on a VM are restored quickly.
Backup testing is an important step in the effectiveness and reliability of the database backup and recovery process. In addition, with testing, we can analyze the backup and recovery for further improvements. It involves verifying the integrity of backup files, testing the restoration process, and evaluating the performance of the backup solution.
Recovery testing is also crucial aspect of database backup and recovery. It involves simulating various failure scenarios to ensure that the database can be successfully restored and recovered in case of data loss or system failures beside with recovery testing we can also test the quality of data and the time efficiency and speed of the recovery process.
Validation of backups is a major step in ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of database backup and recovery processes. It involves verifying the integrity and dependability of backed-up data to ensure its accuracy and completeness. Validating backups helps with data security and detects any potential errors. Validating data is also quite important in making sure that data isn’t redundant.
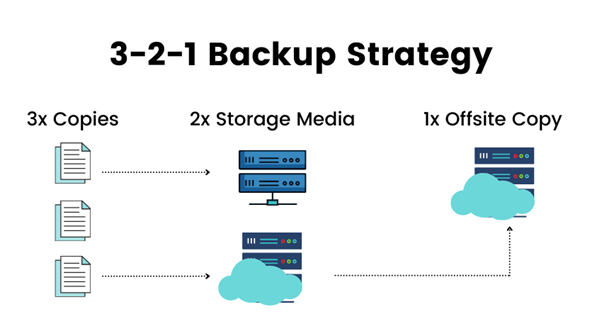
One of the best practices of database backup strategy is according to the 3-2-1 backup rule; businesses should maintain three complete copies of their data: at least one off-site copy and two local copies on various media types. By employing the above-discussed procedures, an organization may backup its data to a local on-premises backup storage system, copy it to another onsite backup storage system, and replicate it to a different location. Even if a collection of storage snapshots depends on the primary storage system’s health and is located on it, it is permissible to consider them as one of the three copies in a contemporary data center.
Based on the database impact and the importance of database backup, a recovery plan is crucial because if a database has a data loss either by natural disaster or error in the system, there will be no way to recover it without any backup and recovery plan. As data loss occurs, the organization or company can’t continue the business operation in need of the lost data. Besides, the recovery process also takes a long time, based on the data that needs to be recovered and recovery performance. This is why having a backup and recovery plan for the database is of the utmost importance: it can make a difference in business operation performance and allow an acceptable time for the system’s recovery.
Keywords: backup, database, recovery, strategy
Reference
https://sis.binus.ac.id/2023/12/01/managing-database-backups-and-disaster-recovery-plan/
https://optimizdba.com/best-practices-for-backup-and-recovery-of-databases/


