Customization Misfit in ERP
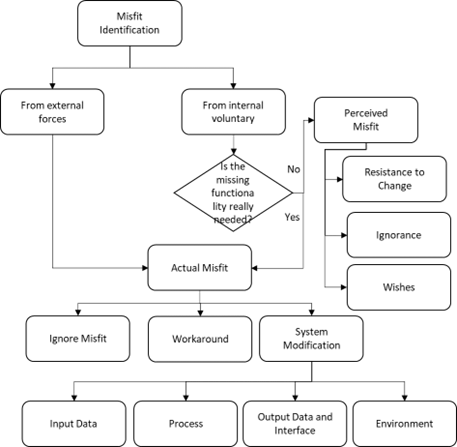
One of the initial activities in implementing an ERP system is to breakdown the organization’s business processes in detail and match them with the process embedded in the ERP system, which is usually called fit-gap analysis. In standard/ vanilla implementation, the organization sets the available parameter in ERP to match with the organization’s business process without making any modification in the system. If the organization’s business process cannot fit with the available parameter, the organization needs to choose between change the organization’s business process or modify the ERP system. This gap between organization business process and system capability is referred to as Misfit. Not every misfit identified in ERP implementation is an actual misfit, rather it can be a perceived misfit. Perceive misfit does not come from legitimate issues, in fact, it derives from user resistance to change, ignorance, and wishes. Resistance to change is a situation where employees want to work the way they do previously in the old system. Thus, the change requests to modify the new system to be like the old system arises. This case happened as the user feel uncertain in the new system. Meanwhile, ignorance is a form of user lack of knowledge toward the new system. User does not try to understand feature that system has, thus they perceive the system has some missing functionality or has lower performance compared to the old system. Lastly, wishes’ is the user’s high expectation toward a new system. The replacement of the old system with the new system leads the user to think that the new system will be far better from the old system in all aspects so that they perceive it as a misfit and want it to be customized.
Previous research stated that misfit could take place in three-level; Country-specific requirement, Industry-specific requirement, and Enterprise specific requirement. Most of the gap happened in enterprise-specific requirements since the ERP was built to accommodate the organization’s business process generalized in the industrys. Four categorizations are; Input data, process, output, and System Environment misfit.
Input Data Misfit is an inability of the ERP system to input various objects or documents into the ERP system database. It includes incompatible data format, poor visibility of data, and poor accuracy of data. This category is a deep structure misfit. Process Misfit is an incompatibility between organization and ERP system in the context of processing procedure. It includes; incompatibility of business strategy, incompatibility to model business process, incompatibility with the structure of the organization. This category is a deep structure misfit. Output data and Interface Misfit is an incompatibility between organization and ERP system in the context of information content and presentation of the output. It includes; incompatible output format of data, poor quality or accuracy of output, incompatible terms and meanings, interface which is irrelevant and complex, and no visibility of output’s logic and calculation. This category is a surface misfit. Lastly, System Environment Misfit represents an incompatibility between system usability and IT Infrastructure. It includes; missing functionalities of non-transactional, poor quality and performance of the system, and poor usability by the community of target user.
The type of misfit and customization are chosen will influence the cost, technical difficulties, and risk. Change in the Input Data and Process misfit requires higher cost, technical difficulties, and risk since these two misfits happened in the core system layer which integrates with other modules. Some ERP vendors do not recommend the organization to access or modify source codes of the system and will not provide maintenance support if there is havoc which caused by those type of modification. Therefore, in this situation, if possible, it is suggested to change the business process rather than system to accommodate Input Data and Process misfit unless the benefit of system modification is greater than business process change. On the other side, the other two types of misfits; Output Data & Interface and System Environment have lower cost, technical difficulties, and risk. Therefore, many system modifications take place in these two categories. Normally ERP consultants are more willing to modify the system to close the gap in the interface or output level. To summarize this step, we developed a flow chart that could guide the organizational to analyze their misfits and help to make decisions.

Source: Wijaya et al., 2021
Reference:
Wijaya, M. I., Suzanna, & Utomo, D. (2021). Enterprise Resource Planning Modification: A Literature Review. ComTech: Computer, Mathematics and Engineering Applications, 12(1), 33-43. https://doi.org/10.21512/comtech.v12i1.6610
Hustad, E., Haddara, M., & Kalvenes, B. (2016). ERP and Organizational Misfits: An ERP Customization Journey. Procedia Computer Science, 100(1877), 429–439. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.09.179
Ashley Davis. (2005). ERP Customization Impacts on Strategic Alignment and System Agility. Proceedings of the 2005 Southern Association of Information Systems Conference
Soh, C., S.S. Kien, and J. Tay-Yap. (2000). Enterprise resource planning: cultural fits and misfits: is ERP a universal solution? Communication of the ACM, 43(4), 47-5. doi: 10.1145/332051.332070
Soh, C., & Sia, S. K. (2004). An institutional perspective on sources of ERP package-organisation misalignments. Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 13(4 SPEC. ISS.), 375–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2004.11.001
Yen, T. S., Idrus, R., & Yusof, U. K. (2011). A framework for classifying misfits between enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and business strategies. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 16(2), 53–75.
Yen, T. S., Idrus, R., & Wong, W. P. (2013). ERP misfit-reduction strategies: A moderated model of system modification and organizational adaptation. Journal of Global Information Management, 21(1), 59–81. doi: 10.4018/jgim.2013010104
Suryanto, Agustinus Dimas Angga. (2018). Changeability of ERP Systems (Master’s Thesis). Radbound University
Van Beijsterveld, Joost & van Groenendaal, Willem. (2015). Solving misfits in ERP implementations by SMEs. Information Systems Journal, 26 (4), doi: 10.1111/isj.12090

