Utilization of Enterprise Resource Planning Systems as the Best Solution for Business Development during the Pandemic and post-pandemic Covid-19
BACKGROUND
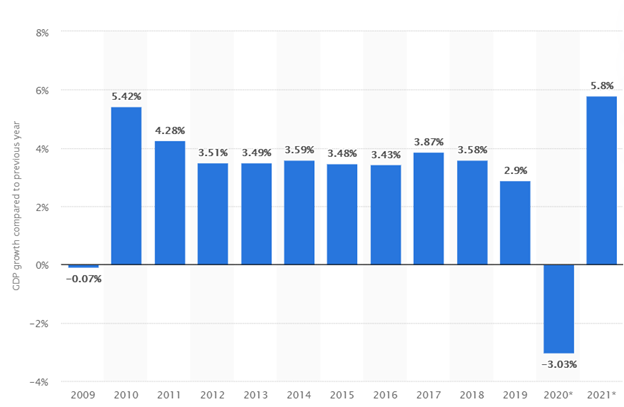
Fig.1 (The world GDP update)
Source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/273951/growth-of-the-global-gross-domestic-product-gdp/
Based on the data above, in 2020, the global economy experienced a very significant decline in the growth of -3.03%. The decrease is caused by the impact of the covid-19 pandemic, which directly imposes all activities or work is done online (work from home). However, in 2021 it is predicted that the global economy will experience a rapid growth increase of 5.8%, which to achieve this, a company must be managed effectively and able to adapt quickly to environmental changes. Therefore, the best solution available for a company in responding to the impact of the covid-19 pandemic is the use of Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, which by using the system, all divisions of the company can be integrated, and also the system supports a company to conduct work from home policies through the Cloud ERP systems feature. The objective and goal of writing this article are to help companies to grow their business during the pandemic and post-pandemic Covid-19 through improving the effectiveness and efficiency of company management by using ERP systems.
LITERATURE
According to O’Brien, J. A., and Marakas, G.M. (2010:272), Enterprise Resource Planning systems are corporate systems consisting of all company functions supported by several integrated software modules to support internal business processes in a company, which according to them, there are 5 main components of an ERP system, namely as follows:
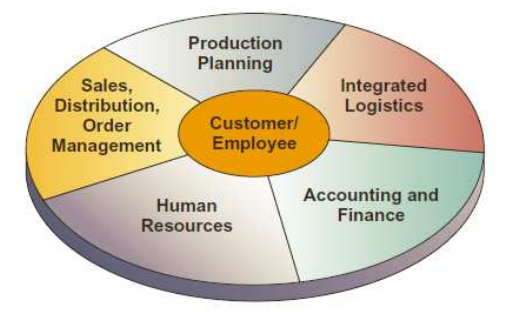
Fig.2 (5 main components of ERP systems)
Source: https://library.binus.ac.id/eColls/eThesisdoc/Bab2/2013-1-00080-SI%20Bab2001.pdf
According to James A. Hall (2011:31), Enterprise Resource Planning systems is an information system model that enables a company to integrate its main business processes. Meanwhile, according to Patricia Wallace, in her book entitled “Introduction to Information systems”, Enterprise Resource Planning systems is a system designed to improve the lack of communication in the functional area of information systems. So, based on the above definitions, it can be concluded that Enterprise Resource Planning systems (ERP systems) are a system developed to connect all functional areas of information systems (such as accounting and finance, Human resources, and others) into one centralized software. To know ERP systems more deeply, the researcher will give examples of cases of the impact of ERP systems implementation on organizations in Indonesia.
RESULT and DISCUSSION
This section discusses the strategic and tactical impact of ERP systems implementation on organizations in Indonesia. The sample taken is as follows:
Table 1. Research sample
| NO. | Industrial Sector | Number of organizations |
| 1. | Telecommunication | 2 |
| 2. | Manufacturing | 3 |
| 3. | Automotive | 1 |
| 4. | Oil and Gas | 1 |
| Total Organization as a sample | 7 | |
Strategic impacts include product excellence, product differentiation, added value, the bargaining power to suppliers/customers, increased entry barrier, and competitiveness support. Tactical impacts include support for the core business, operational efficiency, reduced product costs, good time management, good resource management, increased productivity, community resilience, skills development and restructuring, and human resource development.
The strategic impact of implementing ERP Systems
The survey results in 7 industries that sampled research related to the strategic impact of ERP systems implementation in Indonesia were as many as 83.33% of respondents agreed that ERP systems implementation can provide added value for organizations; 5.56% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can help companies in differentiating products; 5.56% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can improve the quality and quality of the company’s products in the market; 22.22% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can increase bargaining power to customers/suppliers; 16.67% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can increase market barriers; 50% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can improve organizational competitiveness (see figure 3).
Based on the findings obtained, it shows that ERP systems in Indonesia have a significant impact on tactical rather than strategic. That is because most companies in Indonesia only implement ERP modules that only support core businesses. On the other hand, in implementing the ERP system, the company has not made optimal business process improvement (Dantes and Hasibuan, 2010). ERP system implementation tends to be driven by the technology itself rather than the business needs of the organization. that’s the main reason why ERP systems in Indonesia are more influential on tactical levels.
One of the main reasons why companies want to adopt ERP systems is to gain a competitive advantage. However, most ERP systems implementation in Indonesian companies has not been able to create a competitive advantage. That is because, at the time of ERP systems implementation, companies in Indonesia have not made optimal business process improvements. To do so, they need to re-engineer business processes and software changes as per the organization’s business needs. Also, the company must implement several modules that support the strategic level of the organization, such as Business intelligence (BI), Business information warehouse (BW), Supply chain management (SCM), Customer relationship management, and others).
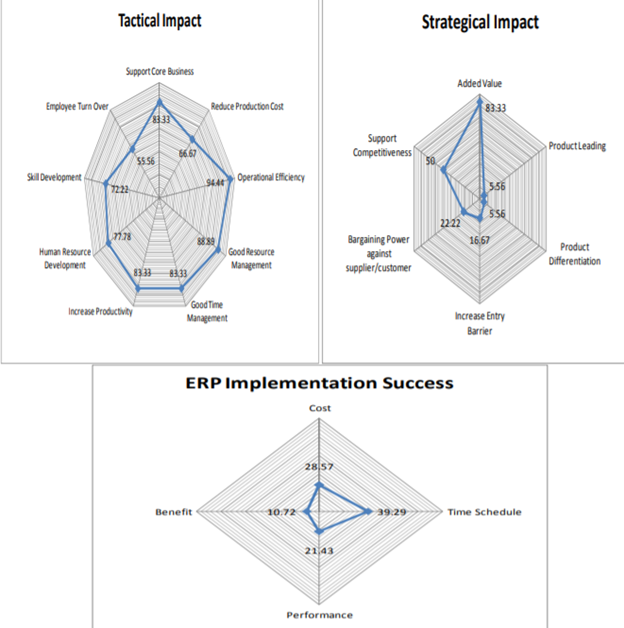
Fig. 3 Survey Result (Strategical and Tactical impact on ERP implementation)
Source: Dantes, G. R. & Hasibuan, Z. A., 2010. The Impact of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) System Implementation on Organization: Case Study ERP Implementation in Indonesia. BIMA Business Review, III(10), pp. 1-10.
The implementation of special modules is expected to be following the company’s business strategy, to have a significant impact on strategic benefits and business continuity in the future. In addition to implementing special modules, the company also needs to implement Business process reengineering (BPR) to optimize business processes to create a competitive advantage (Davenport, 2000; Hammer and Champy, 1993; Somer and Nelson, 2003). However, in Indonesia, BPR is rarely used, especially in government-owned companies. Because BPR can make changes in the company in a radical direction, such as the reduction of employees. Furthermore, BPR can change the company’s business processes that have been implemented for many years, which can directly reduce the overall productivity of employees, because employees must be able to adapt and learn new things.
The ERP implementation approach (BPR drive ERP) is very risky. However, if a company succeeds in implementing it, it will provide optimal benefits as well as competitive advantages (O’Leary, 2000). This is inversely proportional to the ERP drive BPR approach. ERP drive BPR approach has less risk, but this ERP system will only have an impact on the tactical level of managerial and operational levels (O’Leary, 2000).
Tactical Impact of ERP Systems Implementation
The survey results in 7 industries that sampled research related to the tactical impact of ERP systems implementation in Indonesia were as many as 66.67% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can reduce production costs; 88.89% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can manage good resources; 83.33% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can support core businesses; 99.94% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can improve operational efficiency; 83.33% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can improve time efficiency; 83.33% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can increase productivity; 72.22% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can improve skills development; 77.78% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can improve the quality of human resources; 55.56% of respondents agreed that ERP systems can cause employee turnover (see figure 3).
The comparison of data between the impact of ERP systems implementation for the strategic and tactical functions of a company (see figure 3), shows that companies in Indonesia are more likely to utilize ERP systems just to improve the company’s internal processes than to gain strategic advantages. The reason is that:
- The company is not yet ready to invest heavily in implementing all modules of ERP systems, including specific modules;
- Companies are afraid to take big risks, so only choose modules to support core business;
- ERP systems implementation is not driven by the business needs of the organization, but rather driven by the technology itself;
- There are external factors that force companies to implement ERP systems, such as Bank policies, government policies, and others.
One of the interesting things about ERP systems implementation in Indonesia is the high turnover rate of employees. With the increasing quality and skills of employees, employees are motivated to find new jobs that can provide better rewards. This shows that companies in Indonesia are more adhered to the seniority of employees (the number of years employees work in the company) compared to the ability of employees professionally. Therefore, companies often experience tangible losses (e.g., productivity, training costs, and others) and intangible losses (e.g., knowledge). So, the company is forced to look for new employees although it is not yet known if they can fit the system in the company.
Table 2 (Spearman Rank Test Matrix of all variables, N=35)
| Strategical Impact (X1) | Tactical Impact (X2) | |
| ERP implementation Success (Y) | 0,167 (Not significant correlation with p<0,05) | 0,813 (significant correlation with p<0,01) |
The data above shows that the implementation of ERP systems in Indonesia has more impact on tactical benefits than strategic benefits by using only standard ERP modules that support core business activities. It is seen from the data generated from Spearman rank test results that is strategic impact, pyx1 = 0.167 (insignificant with p<0.05), while tactical impact, pyx2 = 0.813 (significant with p<0.01).
SUMMARY/CLOSING
Based on the research that has been done, it can be concluded that ERP systems are very important for a company in increasing tactical and strategic advantages, especially during the Covid-19 Pandemic and post-pandemic covid-19. Strategic impacts include product excellence, product differentiation, added value, the bargaining power to suppliers/customers, increased entry barrier, and competitiveness support. Tactical impacts include support for unit business, operational efficiency, reduced product costs, good time management, good resource management, increased productivity, community resilience, skills development and restructuring, and human resource development.
References
Pletcher, H. 2020. Growth of the Global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) from 2009 to 2021. https://www.statista.com/statistics/273951/growth-of-the-global-gross-domestic-product-gdp/. Accessed January 8, 2021
Moller, Charles. 2004. ERP II – Next-generation extended enterprise resource planning. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268289563_ERP_II_-Next-generation_Extended_Enterprise_Resource_Planning. Accessed January 8,2021.
Binus University. 2018. Enterprise resource planning (ERP). https://library.binus.ac.id/eColls/eThesisdoc/Bab2/2013-1-00080-SI%20Bab2001.pdf. Accessed January 9, 2021.
Patricia Wallace. (2015). Introduction to Information Systems. 2. Pearson Education Limited. England. ISBN: 978-1292071107.
Bradford, M., 2015. Modern ERP: Select, Implement, and Use Today’s Advanced Business Systems. 3rd penyunt. Florida: lulu.com.
Dantes, G. R. & Hasibuan, Z. A., 2010. The Impact of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) System Implementation on Organization: Case Study ERP Implementation in Indonesia. BIMA Business Review, III(10), pp. 1-10.
GRONWALD, K.-D., 2020. Integrated Business Information Systems: A Holistic View of the Linked Business Process Chain ERP-SCM-CRM-BI-Big Data. 2nd penyunt. Lucerne, Switzerland: SPRINGER.
Hanafizadeh, P. & Ravasan, A. Z., 2011. A McKinsey 7S Model-Based Framework for ERP Readiness Assessment. International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems, 7(4), pp. 23-63.
Piazolo, F., Geist, V., Brehm, L. & Schmidt, R., 2017. Key Factors for Successful ERP Implementation: Case Studies from Private and Public Organizations in Thailand. Key Factors for Successful ERP Implementation, 285(10), pp. 3-16.


