Process Costing
Process Costing is a cost calculation system used by companies that produce the same product continuously, where the accounting method tracks and accumulates direct costs, and allocates indirect costs from the manufacturing process. Costs incurred for products, usually in large batches. Finally, costs must be allocated to units of each product.
Processing Departments (Processing departments)
The processing department is the organizational unit where work is performed on the product and where materials, labor, or overhead costs are added to the product. For example, a potato chip factory might have three processing departments – one for preparing the potatoes, one for cooking, and one for checking and packaging. A brick factory may have two processing departments – one for mixing and molding the clay into bricks and another for firing the molded bricks. Some products and services may go through a number of processing departments, while others may go through only one or two. Regardless of the number of processing departments, they all have two important features. First, activities in the processing section are carried out uniformly across all units that pass through it. Second, the output of the processing department is homogeneous; in other words, all units produced are identical.
Sunsport Beverager, Lt. of Fiji makes blended tropical fruit drinks in two stages . Fruit juices are extracted from fresh fruits and then blended in the Blending Department. The blended juices are then bottled and packed for shipping in the Bottling Department. The following information pertains to the operations of the Blending Department for June.
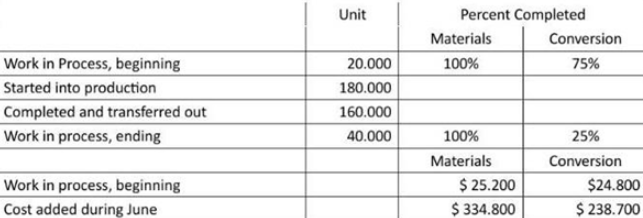
Assume that the company uses the weighted-average method.
- Determine the equivalent units for June for the Blending Department.
|
|
Materials |
Conversion |
|
Transferred to Next Department |
$160.000 |
$160.000 |
|
Ending Work in Process: |
|
|
|
Materials: 40.000 units x 100% complete |
40.000 |
|
| Conversion: 40.000 units x 25% complete |
|
10.000 |
|
Equivalent Units of Production |
$200.000 |
$170.000 |
- Compute the costs per equivalent unit for the Blending Department.
|
|
Materials |
Conversion |
|
Cost of beginning work in process |
$ 25.200 |
$24.800 |
|
Cost added during the period |
334.800 |
238.700 |
|
Total cost (a) |
$ 360.000 |
$ 263.500 |
|
Equivalent unit of production (b) |
200.000 |
170.000 |
|
Cost per equivalent unit (a) + (b) |
$ 1.80 |
$1.55 |
- Determine the total cost of ending work in process inventory and the total cost of units transferred to the Bottling Department.
|
|
Materials |
Conversion |
Total |
|
Ending WIP Inventory |
|
|
|
|
Equivalent units of production |
40.000 |
10.000 |
|
|
Cost per equivalent unit |
1,8 |
1,55 |
|
|
Cost of ending WIP Inventory |
72.000 |
15.500 |
87.500 |
|
Units completed and transferred out: |
|||
|
Units transferred to the next department |
160.000 |
160.000 |
|
| Cost per equivalent unit |
1,8 |
1,55 |
|
|
Cost of units completed and transferred out |
288.000 |
248.000 |
536.000 |
|
|
|
|
|
- Prepare a cost reconciliation report for the Blending Department for June.
|
Cost to be Accounted for: |
|
|
Beginning – Work In Process Inventory ($25.200 + $24.800 = $50.000) |
50.000 |
|
Add: Production during period ($334.800 + $238.700 = $573.800) |
573.800 |
|
Total Cost to be Accounted For |
623.500 |
|
|
|
|
Cost to be Accounted as Follow: |
|
|
Ending – Work In Process Inventory ($72.000 + $15.500 = $87.500) |
87.500 |
|
Cost of Units Completed & Tranferred Out ($288.000 + $248.000 = $536.000) |
536.000 |
|
Total Cost to be Accounted as Follow |
623.500 |


