Enterprise Architecture Activities
Enterprise architecture (EA) is the practice of analyzing, designing, planning and implementing enterprise analysis to successfully execute on business strategies. EA helps businesses structure IT projects and policies to achieve desired business results and to stay on top of industry trends and disruptions using architecture principles and practices, a process also known as enterprise architectural planning (EAP). Enterprise Architecture is accomplished through a management program and an analysis and design method that is repeatable at various levels of scope. Together the EA Program and method provide an ongoing capability and actionable, coordinated views of an enterprise’s strategic direction, business services, information flows, and resource utilization.
As a management program, EA Provides:
- Strategic Alignment: connect goals, activities, and resources
- EA supports strategic planning and other operational resource planning processes by providing macro and micro views of how resources are to be leveraged in accomplishing the goals of the enterprise.
- Standardized Policy: Resource governance and implementation
- EA supports the implementation of standardized management policy pertinent to the development and utilization of IT and other resources.
- Decision Support: Financial control and configuration management
- EA provides support for IT resource decision-making at the executive, management and staff levels of the enterprise. At the executive level, EA provides visibility for large IT initiatives and supports the determination of strategic alignment. At the management level, EA supports design and configuration management decisions, as well as the alignment of IT initiatives with technical standards for voice, data, and security. At the staff level, EA supports decisions regarding operations, maintenance, and the development of IT resources and services.
- Resource Oversight: Lifecycle to development/management
- EA supports standardized approaches for overseeing the development of capabilities and optimizing supporting resources. Depending on the scope of the resources involved and the available timeframe for development, various system development lifecycle methods cam be used to reduce the risk that cost, schedule, or performance parameters may not be met.
As an analysis and design method, EA Provides:
- EA Approach: The framework, analysis/design method, and artefact set
- Current Views: Views of as-is strategies, processes, and resources
- Future Views: Views of to-be strategies, processes, and resources
- EA Management Plan: A plan to move from the current to the future EA
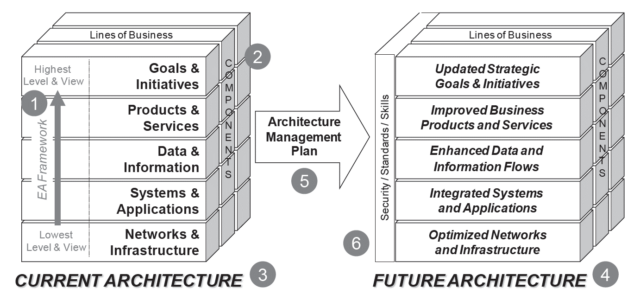
EA analysis and design are accomplished through the following six basic elements: (1) An EA Documentation framework, and (2) an implementation methodology that support the creation of (3) current and (4) future views of the architecture, as well as the development of (5) an EA Management Plan to manage the enterprise’s transition from current to future architectures. There are also several areas common to all levels of the framework that are referred to as (6) “threads” as shown in this figure:
References
Scott A. Bernard. (-). An Introduction to Enterprise Architecture. 03. Authorhouse. Bloomington. ISBN: 978-1-4772-5800-2.
The Five Activities of Enterprise Architecture. (2020). Retrieved 24 February 2020, from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/five-activities-enterprise-architecture-matthew
Architecture Activities – Enterprise Architecture. (2020). Retrieved 24 February 2020, from http://iea.wikidot.com/architecture-activities