Enterprise Architecture Planning
Enterprise Architecture Planning (EAP) is a method used to build the information architecture. According to Steven H Spewak, EAP is a business and architecture definition, not a business design and architecture. EAP is an architecture in data architecture, application and technology required to support the organization’s business. Steven H Spewak stated that the architecture here is intended like a blueprint, drawing, or model.
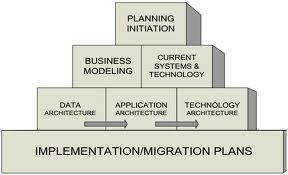
Steven H. Spewak EAP methodology divides into seven components where the components are grouped by logical layers shaped wedding cake. As shown in Figure 1 below, the components are grouped into 4 layers, where each layer presents a different task focus.
Figure 1. Components of EAP
- Planning Initiation : initial stages that must be done is to initiate planning, with the hope of this architectural model building process can be directed very well. This stage as the foundation for the subsequent stages of processing. This early stage is important, especially because at this stage the scope and planning of activities or work plan is defined, define the methodology to be used, the resources involved and assign devices (tools) that will be used. Another factor is the support and commitment from management, which is not only in verbal form, but the effect on the resources (personnel, budget and time) to carry out the entire process.
- Business Modeling : draw up a basic knowledge of business and information used in conducting business activities. The purpose of this business model is to provide the basis of a complete and thorough knowledge that can be used to define the architecture and implementation plan. There are three stages to the business model, as follows:
- Documentation ofthe organizational structure.
- Identificationanddefinition ofbusiness functions.
- Documentation ofthe mainbusinessmodels, distribution, andpresentation toallthe business communitytolisten to thecommentary
Survey enterprise: survey aims to obtain a complete description of the business model that includes such things as the following:
- What information isusedto createafunction
- Whenthe function isformed.
- Wherethe function isformed.
- How oftenfunctionis formed.
- What opportunitiesexisttoimprovefunction.
- Data Architecture : define the main types of data required to support the business activities. Data architecture consists of data entities, where each data has attributes and relationships to other data. Guidance in defining the architecture of the data, namely:
- Registercandidatesby reviewingthe dataentity’s business model and thedescription of the systemandthe technology used.
- Setthe entitythatwill be used.
- Defineand documenteachof these entities(ER Diagram).
- Connect thedata entitywitha detailedbusiness functions.
- Implementation/Migration Plans : defining the stages for the implementation of applications, scheduling implementation, analysis of cost / benefit and determine a clear path to move from the current position to the desired position in the future, new information systems organization, the adoption of new systems development methodology, and setting standards or procedures. The planning stages of implementation, among others:
- Determinethe sequence ofapplications to be built.
- Measurethe business, the abilityof available resourcesanddesigningstages ofimplementationschedule.
- Determiningfactors ofsuccessandgenerateappropriate recommendations.
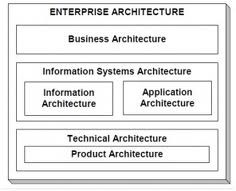
Figure 2. Enterprise Architecture
Reference :
https://www.revolvy.com/topic/Enterprise%20architecture%20planning