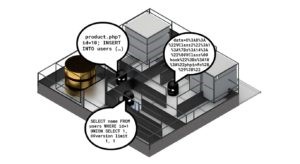
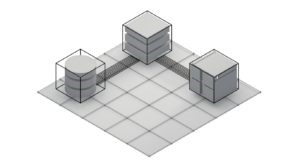
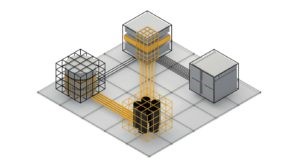
Example of Database Security
INTRODUCING ACRA – An Open Source Database Security Suite
If you are concerned about data security, this means confronting a threat landscape that requires vigilance and defence against a wide range of attacks. One of the prime targets for attack continues to be sensitive data that is stored in backend database storage. From simple discovery of unsecured databases, through classic SQL injection techniques, to compromised infrastructure that allows wholesale copying of database content, attacks focus on data assets with increasing precision.
Your app, your defences, your adversaries
Acra from Cossack Labs offers a range of novel and well established techniques designed to protect sensitive data stored in backend database systems. Acra provides these as a suite of database protection tools that are easy to use, deploy and automate.
Acra provides three key features enabling you to:
- selectively protect sensitive records with a strong, proven cryptographic scheme.
- monitor the request flow to the database to prevent malicious requests.
- deploy these security features in a well-compartmented infrastructure, where risks and attack surfaces are known and understood.
Acra can be deployed in both traditional database-frontend web services and large, microservice-rich infrastructures. Unlike many other database encryption tools, Acra integrates with your existing infrastructure without the need to rebuild components to add the security layer. Additionally, Acra’s selective encryption capabilities can integrate not just with your applications but also migration scripts, archival data dumps and indeed any procedure that involves database requests.
Acra is built using GoLang and currently supports PostgreSQL databases and Ruby, Python, PHP, Node.js or GoLang application development environments. Acra is licensed as Apache 2 open source software.
How does Acra work?
Role architecture (L->R): backend, middleware, front-end
Acra enables front-end application code to selectively encrypt data with a set of encrypt-only keys. The encrypted data is then transmitted (via an AcraProxy service) to the database. Requests to access the data are routed through an AcraServer – a network service that contains the decryption keys, decrypts the data and forwards the response to the application over a secure connection. Additionally, the AcraServer can be configured to detect unexpected requests and take appropriate action.
Role architecture with Acra components
So, by using Acra, you can more secure your company database because Acra provide full protection with encryption on your data. So, it’s more difficult for hackers to hack your company database.
References:
- Connolly & Begg, Database Systems: A Practical Approach to Design, Implementation and Management
- https://www.techopedia.com/definition/29841/database-security
- http://www.brighthub.com/computing/smb-security/articles/61554.aspx
- https://www.informationsecuritybuzz.com/articles/introducing-acra-open-source-database-security-suite/