Arsitektur Datawarehouse
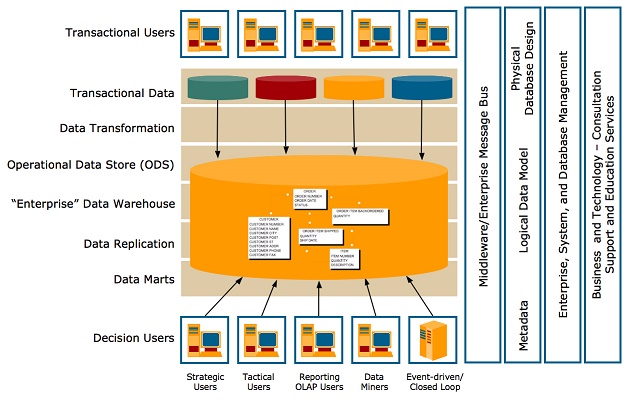
The data warehouse is a collection of integrated, subject-oriented databases design to support DSS functions, where each unit of data is non-volatile and relevant to some moment in time.
Characteristics of Data Warehousing
- Subject oriented, data are organized by organized. Subject orientation provides a more comprehensive view of the organization
- Integrated, DW must place data from different source into consistent format.
- Time variant, a warehouse maintains historical data. The data do not necessarily provide current status.
- Nonvolatile, after data entered into a data warehouse, user can’t change or update data.
Data Mart is a departmental data warehouse that stores only relevant data.
- Dependent data mart
A subset that is created directly from a data warehouse
- Independent data mart
A small data warehouse designed for a strategic business unit or a department
Data Warehousing Architectures
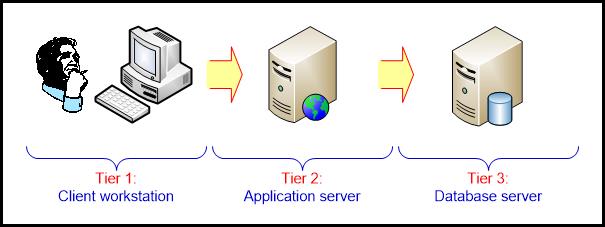
- Three-tier architecture
- Data acquisition software (back-end)
- The data warehouse that contains the data & software
- Client (front-end) software that allows users to access and analyze data from the warehouse
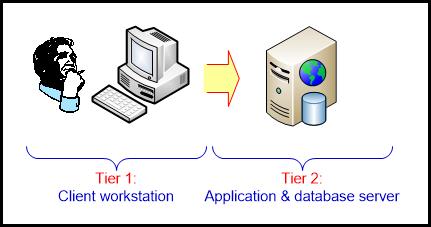
- Two-tier architecture
First 2 tiers in three-tier architecture is combined into one.
Ten factors that potentially affect the architecture selection decision:
- Information interdependence between organizational units
- Upper management’s information needs
- Urgency of need for a data warehouse
- Nature of end-user tasks
- Constraints on resources
- Strategic view of the data warehouse prior to implementation
- Compatibility with existing systems
- Perceived ability of the in-house IT staff
- Technical issues
- Social/political factors
- Data integration Integration that comprises three major processes: data access, data federation, and change capture.
- Enterprise application integration (EAI) A technology thatprovides a vehicle for pushing data from source systems into a data warehouse
- Enterprise information integration (EII) An evolving tool space that promises real-time data integration from a variety of sources
- Service-oriented architecture (SOA) A new way of integrating information systems
- Direct benefits of a data warehouse
- Allows end users to perform extensive analysis
- Allows a consolidated view of corporate data
- Better and more timely information
- Enhanced system performance
- Simplification of data access
- Indirect benefits of data warehouse
- Enhance business knowledge
- Present competitive advantage
- Enhance customer service and satisfaction
- Facilitate decision making
- Help in reforming business processes
- Types of Data Warehouse
Information processing, analytical processing, and data mining are the three types of data warehouse applications that are discussed below:
- Information Processing – A data warehouse allows to process the data stored in it. The data can be processed by means of querying, basic statistical analysis, reporting using crosstabs, tables, charts, or graphs.
- Analytical Processing – A data warehouse supports analytical processing of the information stored in it. The data can be analyzed by means of basic OLAP operations, including slice-and-dice, drill down, drill up, and pivoting.
- Data Mining – Data mining supports knowledge discovery by finding hidden patterns and associations, constructing analytical models, performing classification and prediction. These mining results can be presented using visualization tools.